Introduction
A. Brief Overview of the Ingrown Hair Condition
Ingrown hairs are a common skin condition wherein the hair grows back into the skin instead of rising up from it [1]. This usually occurs when the hair has been cut, and instead of growing outwards, it curls back or grows sideways into the skin, leading to inflammation, redness, and sometimes, infection [2]. While it can occur on any part of the body where hair is removed (such as the face, neck, armpits, chest, back, and pubic area), the focus of this article is on ingrown hair on the labia, a problem that many women encounter but is seldom discussed.
B. The Relevance of Understanding Ingrown Hair on Labia
The labia, being part of the sensitive genital area, are prone to ingrown hairs, especially in individuals who shave, wax, or use other hair removal methods [3]. When the hair in this region is cut or removed, it can sometimes curl back and re-enter the skin, causing discomfort and often worry due to its location. Moreover, due to their appearance, ingrown hairs on the labia can be mistaken for other skin conditions like genital warts or even genital herpes, leading to unnecessary stress and anxiety. Therefore, it becomes highly pertinent to understand, identify, and know how to treat ingrown hair on the labia to maintain good personal hygiene and avoid potential complications.
Identifying Ingrown Hair on Labia
A. Description of Ingrown Hair on Labia
Ingrown hairs on the labia generally appear as small, raised bumps or lumps that are often red or pink in color. In some cases, they can form a pustule or blister filled with pus. The area around the ingrown hair may be painful or itchy, and one might also notice a hair trapped beneath the surface of the skin.
B. Comparison to other skin conditions: Genital Herpes and Genital Warts
Confusion often arises between ingrown hairs, genital herpes, and genital warts due to their similar appearance. Genital herpes is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) that usually presents as small blisters or sores. While they can appear similar to ingrown hairs, they tend to be more painful and can be accompanied by other symptoms such as fever and general discomfort [4].
Genital warts, on the other hand, are caused by certain strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV). They appear as flesh-colored or gray growths that may be smooth or have a cauliflower-like appearance, a distinguishing feature from ingrown hairs.
C. Importance of Accurate Identification
Accurate identification of ingrown hairs is crucial for effective treatment. Misdiagnosis could lead to unnecessary worry and inappropriate treatment. For instance, confusing an ingrown hair for genital herpes or warts could lead to undue anxiety and unnecessary treatments. It’s always best to consult a healthcare professional if you are unsure about any unusual lumps or bumps in the genital area.
Causes of Ingrown Hair on Labia
A. Hair Growth Cycle
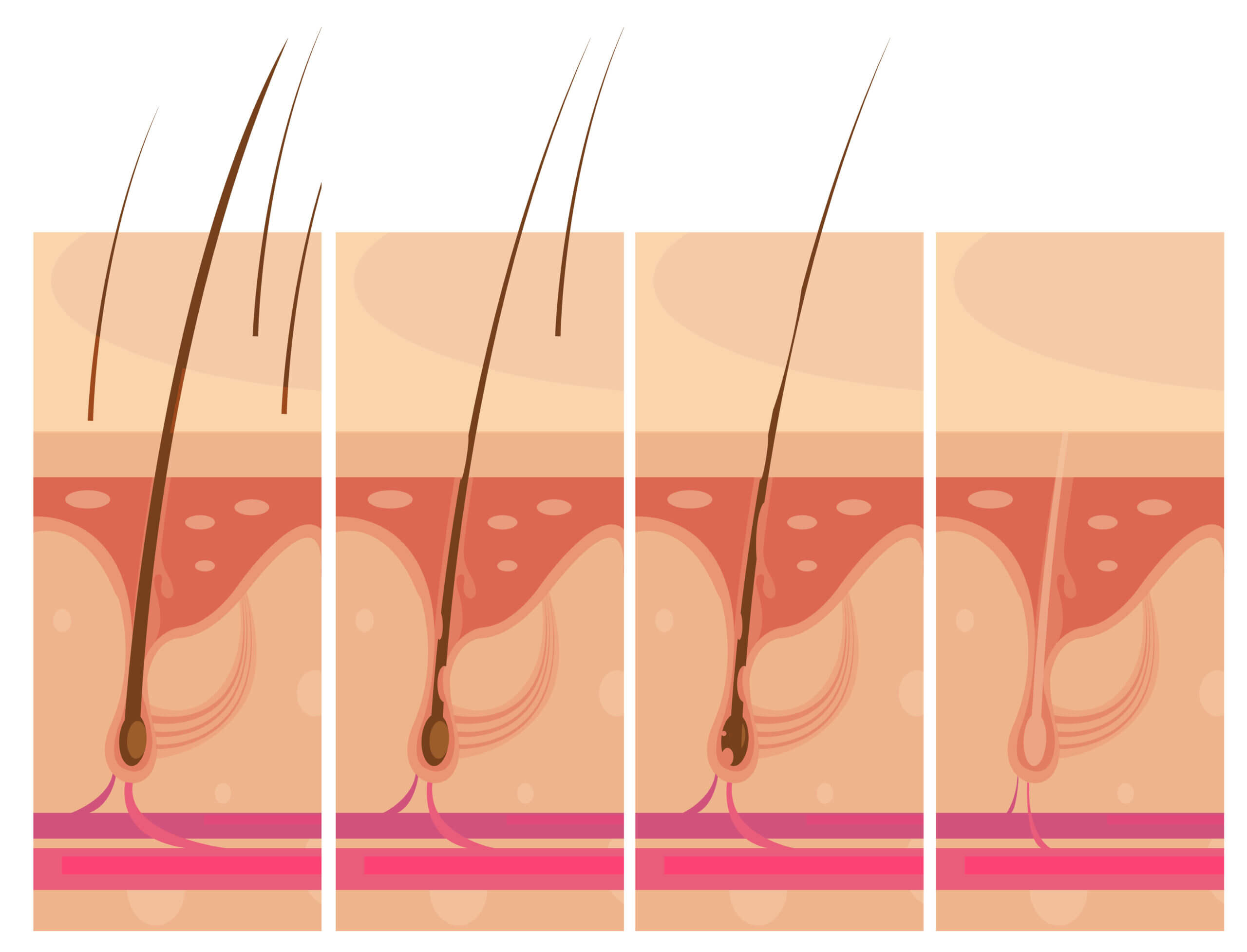
Understanding the hair growth cycle is crucial in grasping why ingrown hairs develop. Hair grows from follicles present under the skin and typically grows straight up and out of the follicle opening. However, in some cases, the hair can curl back into the follicle or grow sideways under the skin, leading to an ingrown hair [5].
B. Factors Contributing to Developing Ingrown Hairs
Several factors can contribute to developing ingrown hairs on the labia:
- Dead Skin Cells: Accumulation of dead skin cells can block the hair follicle, forcing the hair to grow sideways or back into the skin instead of straight out. Regular exfoliation can help prevent this.
- Tight Clothing: Wearing tight underwear or clothing can increase the risk of ingrown hairs. The friction and pressure from tight clothing can push the hair back into the skin, particularly after hair removal.
- Incorrect Hair Removal Techniques: Shaving, waxing, or plucking can also lead to ingrown hairs. Shaving too close to the skin creates sharp-edged hair that can more easily penetrate the skin, while waxing and plucking can cause the hair to break below the skin level, leading to potential ingrown hairs.
Pictures: Visual Guide to Identifying Ingrown Hair on Labia
A. Characteristics of Ingrown Hair on Labia Pictures
The primary visual identifier of an ingrown hair on the labia is a small, red bump that is sometimes filled with pus. This bump often has a hair visible at the center or the hair might be seen curling back into the skin. It may be slightly raised and could be tender to the touch. The skin surrounding an ingrown hair might appear darker, especially in individuals with darker skin tones [6].
B. Distinguishing Ingrown Hair from Genital Herpes and Genital Warts
Identifying ingrown hair on the labia can be particularly tricky as they may be confused with conditions such as genital herpes and genital warts. While ingrown hairs are typically singular and have a hair visible in the center, genital herpes usually presents as a cluster of fluid-filled blisters that rupture to form painful sores [7]. Genital warts, on the other hand, usually form as small, flesh-colored bumps that can grow in clusters with a cauliflower-like appearance. They are generally painless but may itch [8]. Visual diagnosis should always be followed by medical consultation for accurate identification.
Treatment Options for Ingrown Hair on Labia
A. Home Remedies
Simple home remedies can help alleviate the discomfort of an ingrown hair on the labia. These remedies involve:
- Warm Compress: Applying a warm compress to the area can soften the skin and help draw the ingrown hair out.
- Exfoliation: Gently exfoliating the area can remove dead skin cells and help the trapped hair break through the skin.
- Over-the-counter treatments: Products containing salicylic acid or glycolic acid can help treat the ingrown hair by exfoliating the skin and reducing inflammation.
B. Medical Procedures like Laser Hair Removal
For those who frequently experience ingrown hairs, professional treatments like laser hair removal may be a viable option. Laser hair removal uses concentrated light to destroy hair follicles, preventing or reducing hair growth. This can significantly decrease the chance of developing ingrown hairs [9].
C. When to Seek Professional Medical Help
While ingrown hairs often resolve on their own, professional medical help should be sought if the ingrown hair:
- Is recurrent or numerous [10].
- Becomes infected (signs include severe redness, swelling, pus, and fever) [11].
- Causes significant pain or discomfort.
- Is a cause of concern or distress due to its appearance [12].
Prevention of Ingrown Hair on Labia
A. Proper Hair Removal Techniques
Certain techniques can be implemented during hair removal to prevent the occurrence of ingrown hairs:
- Pulling the Skin Taut During Shaving: Stretching the skin taut while shaving can provide a cleaner cut and prevent the hair from retracting below the skin surface and growing inward.
- Using a Sharp, Single-bladed Razor: A sharp, single-blade razor is preferable over multi-blade razors for preventing ingrown hairs. It’s important to replace the razor or blade regularly to ensure it remains sharp.
- Shaving in the Direction of Hair Growth: Shaving in the direction that the hair grows (not against it) can reduce the risk of ingrown hairs.
B. Tips for Preventing Ingrown Hairs in the Genital Area
Apart from proper hair removal techniques, there are other ways to prevent ingrown hairs in the genital area:
- Regular Exfoliation: Regularly exfoliating the skin can help remove dead skin cells that can clog hair follicles and contribute to ingrown hairs.
- Wearing Loose Underwear: Wearing loose, breathable underwear can prevent friction and pressure that can push hairs back into the skin [13].
C. Role of Lifestyle Changes
Maintaining good hygiene and skin health is crucial in preventing ingrown hairs. A diet rich in essential nutrients for skin health, as well as keeping the skin hydrated, can contribute to a healthier hair growth cycle and decrease the likelihood of ingrown hairs [14].
Misconceptions about Ingrown Hair on Labia
A. Difference Between Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) and Ingrown Hair
There is often a misconception that ingrown hairs on the labia are a sign of a sexually transmitted infection (STI), such as genital herpes or genital warts. However, it is important to understand that these conditions have distinct characteristics. For instance, while ingrown hairs usually present as singular bumps with a visible hair in the center, genital herpes typically appears as clusters of blisters that rupture to form painful sores [15]. Genital warts are small, flesh-colored bumps that can grow in clusters with a cauliflower-like appearance. Therefore, while these conditions may visually resemble one another, they are fundamentally different and require different treatments.
B. Misconception About Sexual Contact Leading to Ingrown Hairs
Another common misconception is that sexual contact can directly lead to ingrown hairs. While it is true that friction from sexual activity can exacerbate the situation if one is already prone to ingrown hairs, sexual contact in itself does not cause ingrown hairs. Ingrown hairs are more closely related to hair removal methods, the hair growth cycle, and individual skin and hair characteristics.
A. Summary of Key Points
Ingrown hairs on the labia are a common condition that can cause discomfort, but they are generally not a cause for significant concern [16]. They occur when a hair that has been shaved, waxed, or plucked grows back into the skin, causing inflammation and a pimple-like bump. These can be identified by their characteristic appearance, often distinguished from similar conditions such as genital herpes and genital warts through visual examination.
Treatment options range from home remedies like warm compresses and exfoliation to professional treatments like laser hair removal. However, the best approach is often prevention, through methods like correct shaving techniques and lifestyle changes. Lastly, while it’s important to note that ingrown hairs are different from STIs, any persistent or worrisome symptoms should be evaluated by a healthcare provider .
B. The Importance of Awareness and Appropriate Intervention for Ingrown Hair on Labia
Awareness and knowledge about ingrown hairs on the labia are essential for effective management and prevention of the condition. Understanding the cause, identification, treatment, and prevention strategies can help individuals make informed decisions about their health. Furthermore, dispelling misconceptions about the condition can reduce anxiety and unnecessary fear related to sexually transmitted infections [17].