Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. With proper care and management, individuals with diabetes can lead healthy and fulfilling lives. This article will discuss how diabetes can be managed effectively at home and provide essential guidelines for individuals who want to take control of their health.
Introduction to Diabetes Management
Diabetes management involves a combination of lifestyle choices, medication, and monitoring blood sugar levels. The primary goal is to keep blood sugar levels within a target range as recommended by healthcare professionals. By managing diabetes effectively, individuals can prevent or delay complications associated with the condition.
Types of Diabetes
There are two main types of diabetes:
- Type 1 diabetes: This is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. As a result, individuals with type 1 diabetes require insulin injections to regulate their blood sugar levels.
- Type 2 diabetes: This is the most common form of diabetes and occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or does not produce enough insulin. Lifestyle factors, such as poor diet and lack of physical activity, contribute significantly to the development of type 2 diabetes.
Importance of Diabetes Management
Effective diabetes management is crucial in preventing or delaying complications associated with the condition. Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to severe health problems, including heart disease, stroke, kidney damage, nerve damage, and vision loss. By keeping blood sugar levels within the target range, individuals with diabetes can reduce their risk of developing these complications.
1. Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
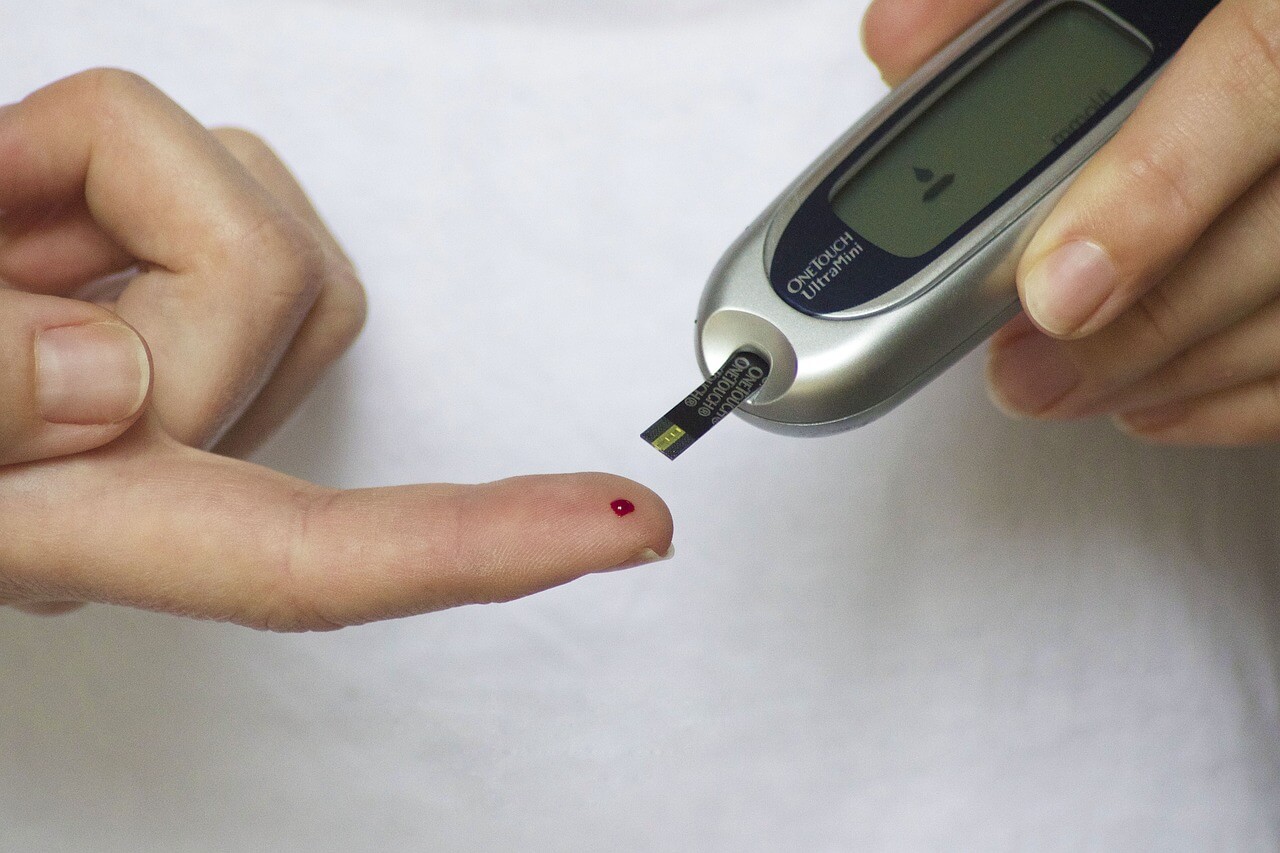
Regularly monitoring blood sugar levels is a critical aspect of diabetes management. By keeping track of blood sugar levels, individuals can better understand how different factors affect their blood sugar and make necessary adjustments to their treatment plan.
How to Monitor Blood Sugar Levels
There are several ways to monitor blood sugar levels:
- Blood glucose meter: This is the most common method used to check blood sugar levels at home. Individuals with diabetes can use a blood glucose meter to measure their blood sugar levels by pricking their finger and placing a drop of blood on a test strip.
- Continuous glucose monitor (CGM): A CGM is a device that measures blood sugar levels continuously throughout the day. It involves wearing a sensor under the skin, which sends real-time glucose readings to a monitoring device.
When to Check Blood Sugar Levels
The frequency of blood sugar monitoring depends on the type of diabetes and the individual’s treatment plan. Generally, individuals with type 1 diabetes should check their blood sugar levels more frequently than those with type 2 diabetes. It is essential to consult with healthcare professionals to determine the appropriate monitoring schedule.
2. Medication Management
Medication plays a critical role in diabetes management, particularly for individuals with type 1 diabetes who require insulin injections. It is crucial to follow the prescribed medication regimen and consult with healthcare professionals to adjust dosages as needed.
Types of Medications
There are various medications available to help manage diabetes:
- Insulin: Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. Individuals with type 1 diabetes and some with type 2 diabetes require insulin injections or insulin pump therapy to maintain their blood sugar levels within the target range.
- Oral medications: For individuals with type 2 diabetes, oral medications can help improve blood sugar control. These medications work in various ways, such as increasing insulin production, reducing glucose production in the liver, or improving insulin sensitivity.
- Non-insulin injectable medications: Some non-insulin injectable medications can help with blood sugar management in individuals with type 2 diabetes, such as GLP-1 receptor agonists and amylin analogs.
Medication Adherence
It is crucial to follow the prescribed medication regimen and take medications at the correct times and dosages. Skipping or altering medication dosages can result in uncontrolled blood sugar levels and increase the risk of complications. Communicate with healthcare professionals to address any concerns or side effects related to medications.
3. Healthy Eating Habits
A balanced diet plays a critical role in diabetes management. By making healthy food choices, individuals with diabetes can maintain blood sugar levels within the target range and support overall health.
Carbohydrate Counting and Portion Control
Carbohydrates have the most significant impact on blood sugar levels. Learning how to count carbohydrates and control portion sizes is an essential skill for managing diabetes effectively. Some key tips include:
- Use measuring cups or a food scale to ensure accurate portion sizes.
- Familiarize yourself with the carbohydrate content of different foods.
- Plan balanced meals that include a mix of carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats.
Food Choices
Opt for nutrient-dense, low-glycemic-index foods that help maintain stable blood sugar levels. Some healthy food choices for individuals with diabetes include:
- Whole grains, such as brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat pasta
- Fruits and vegetables, particularly non-starchy vegetables like leafy greens, broccoli, and cauliflower
- Lean protein sources, such as chicken, turkey, fish, and tofu
- Healthy fats, including avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil
Meal Planning and Scheduling
Coordinating meals and medication schedules is crucial in diabetes management. Ensure that meals are well-balanced and consumed at consistent times to avoid fluctuations in blood sugar levels.
4. Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is essential for overall health and diabetes management. Exercise helps the body use insulin more efficiently and lowers blood sugar levels.
Exercise Recommendations
Consult with healthcare professionals to determine the appropriate exercise plan. In general, adults should aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity per week, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling.
Exercise Precautions
Individuals with diabetes should take precautions when exercising:
- Check blood sugar levels before, during, and after exercise.
- Stay hydrated by drinking water or other sugar-free fluids.
- Be prepared with a small snack or glucose tablets in case of low blood sugar levels.
5. Stress Management
Stress can negatively impact blood sugar levels, making diabetes management more challenging. Implementing stress-reducing techniques can help maintain blood sugar control and improve overall well-being.
Stress Reduction Techniques
Some effective stress reduction techniques include:
- Deep breathing exercises
- Meditation or mindfulness practices
- Physical activity, such as yoga or walking
- Seeking support from friends, family, or mental health professionals
6. Diabetes Management During Illness
Illness can complicate diabetes management due to changes in appetite, activity levels, and the body’s production of stress hormones. It is essential to have a sick-day plan in place to maintain blood sugar control during illness.
Sick-Day Plan
A sick-day plan should include:
- Instructions on medication adjustments
- Guidelines for monitoring blood sugar and ketone levels
- When to contact healthcare professionals for guidance
Maintaining Blood Sugar Control During Illness
To maintain blood sugar control during illness:
- Continue taking diabetes medications as prescribed, unless directed otherwise by healthcare professionals.
- Stick to the diabetes meal plan and stay hydrated with water or sugar-free fluids.
- Monitor blood sugar levels more frequently, as they may fluctuate during illness.
7. Alcohol Consumption and Diabetes
Alcohol can affect blood sugar levels and interfere with diabetes management. Individuals with diabetes should consume alcohol in moderation and be aware of potential blood sugar fluctuations.
Alcohol Guidelines
If approved by healthcare professionals, individuals with diabetes can consume alcohol in moderation:
- No more than one drink per day for women and men over 65
- No more than two drinks per day for men under 65
Alcohol Precautions
When consuming alcohol, individuals with diabetes should:
- Consume alcohol with food to prevent low blood sugar levels
- Choose lower-calorie, lower-carbohydrate alcoholic beverages, such as light beer or dry wine
- Monitor blood sugar levels closely, as alcohol can cause fluctuations
8. Diabetes Management and Women’s Health
Hormonal fluctuations during menstruation and menopause can affect blood sugar levels in women with diabetes, making diabetes management more challenging.
Menstruation and Diabetes
To manage blood sugar fluctuations during menstruation:
- Track blood sugar levels to identify patterns related to the menstrual cycle
- Consult with healthcare professionals to adjust diabetes treatment plans as needed
Menopause and Diabetes
During menopause, women with diabetes should:
- Monitor blood sugar levels more frequently
- Discuss potential hormone replacement therapy options with healthcare professionals to manage menopausal symptoms and blood sugar fluctuations
9. Diabetes Management and Travel
Travel can disrupt routines and affect blood sugar control. Planning and preparation are essential to maintain diabetes management during travel.
Travel Tips for Diabetes Management
- Pack extra diabetes supplies, including medications, glucose monitoring equipment, and snacks
- Keep medications and supplies in carry-on luggage to avoid temperature extremes and potential loss
- Adjust medication schedules and meal plans to accommodate time zone changes
- Monitor blood sugar levels more frequently during travel
10. Ongoing Diabetes Support and Education
Continued education and support are vital in maintaining effective diabetes management. Stay informed about new diabetes treatments, technologies, and research to optimize blood sugar control and overall health.
Diabetes Education Resources
- Seek guidance from healthcare professionals, including endocrinologists, diabetes educators, and dietitians
- Participate in diabetes support groups or online communities to connect with others living with diabetes
- Stay up-to-date with the latest diabetes research and advancements
In conclusion, effective diabetes management requires a combination of blood sugar monitoring, medication management, healthy eating habits, regular physical activity, stress reduction, and ongoing education and support. By taking control of their health and making informed decisions, individuals with diabetes can successfully manage their condition at home and lead healthy, fulfilling lives.