Introduction
A. Definition of Ingrown Hair
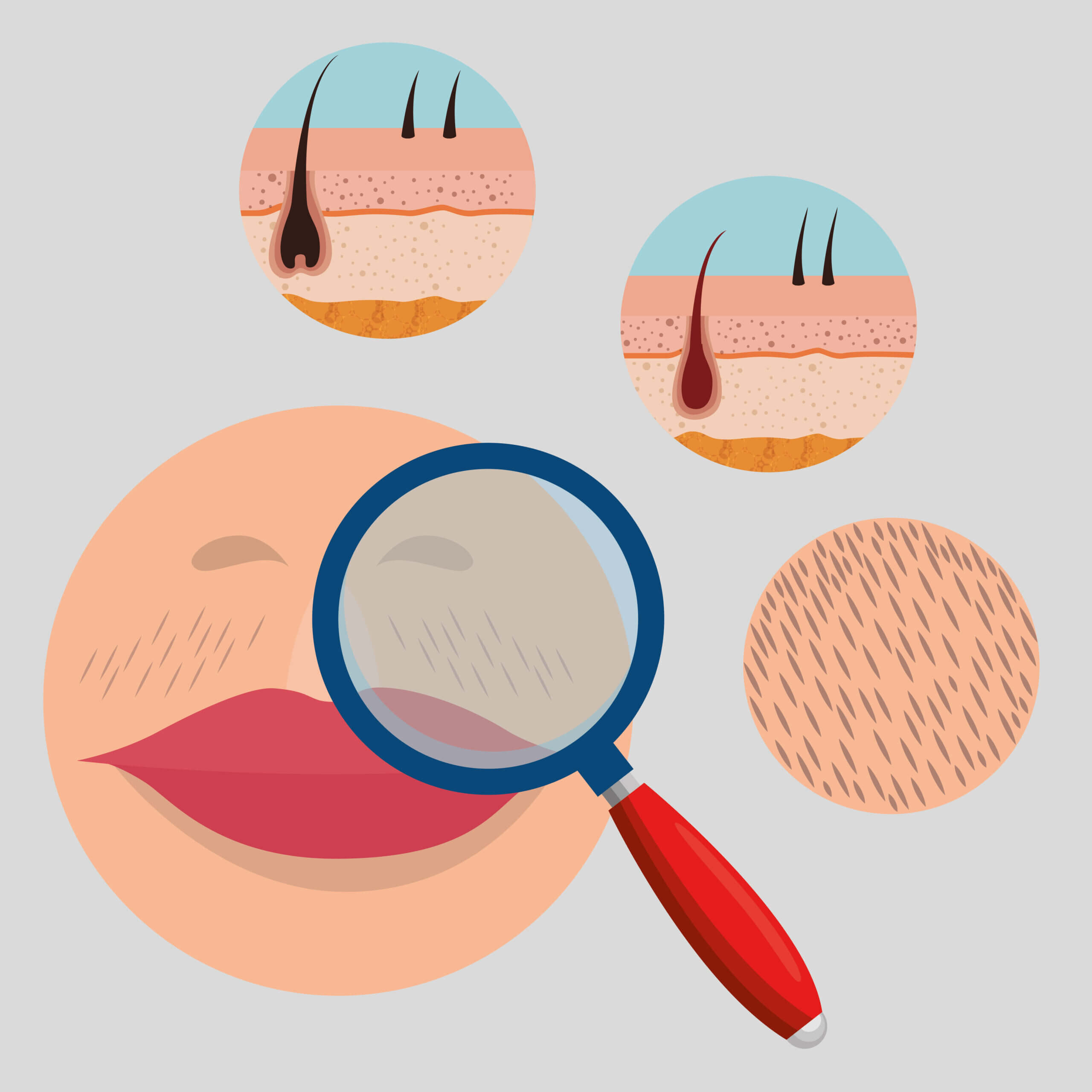
An ingrown hair refers to a hair that has curled back on itself and started growing back into the skin, rather than rising up from it [1]. This condition, scientifically termed pseudofolliculitis, occurs when the sharp tip of a hair pierces the skin and begins growing sideways or downwards [2]. Ingrown hairs can cause discomfort, leading to inflammation, pain, itchiness, and sometimes, a pustule or papule formation at the site [3].
B. Occurrence of Ingrown Hair under the Breast
Ingrown hairs can occur on any part of the body where hair growth exists. An often overlooked area is under the breast, where conditions can sometimes favor ingrown hair formation [4]. Ingrown hairs under the breast, while not as common as other areas such as the face or legs, can occur due to factors like improper hair removal techniques, hormonal imbalances, and specific skin conditions.
Causes of Ingrown Hair under the Breast
A. Improper Hair Removal Techniques
Ingrown hair under the breast is often a result of improper hair removal techniques. Shaving, waxing, or plucking can lead to hair breaking off beneath the skin surface, causing the hair to grow sideways into the skin rather than out of the follicle [5].
B. Hormonal Imbalances
Hormonal imbalances may also contribute to the development of ingrown hairs under the breast. For example, conditions like Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), which lead to increased hair growth (hirsutism), can increase the risk of ingrown hairs [6].
C. Skin Conditions
Certain skin conditions such as keratosis pilaris, which causes small, hard bumps to appear on the skin, may increase the likelihood of ingrown hairs under the breast [7]. These bumps can block the hair follicles, causing the hair to grow inward.
D. Sweat Gland Blockage
Sweat glands located under the breast can become blocked, creating a favorable environment for ingrown hairs. The moist, warm environment can cause hairs to curl back into the skin, especially if the area is not kept clean and dry.
E. Tight Clothing
Tight clothing, particularly undergarments that do not fit properly, can contribute to the occurrence of ingrown hairs under the breast. The constant friction and lack of ventilation can cause hair to grow back into the skin.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Ingrown Hair under the Breast
A. Visible Signs
Visible signs of an ingrown hair under the breast may include redness, swelling, and the presence of a raised, pimple-like bump at the site. In some cases, one may be able to see the hair looped back into the skin. Over time, these symptoms might escalate into the development of pus-filled lesions known as pustules.
B. Physical Discomfort
Physical discomfort may accompany an ingrown hair under the breast. The area may be tender to touch and might cause itching or pain. Additionally, the ingrown hair may become inflamed, leading to further discomfort [8].
C. Misdiagnosis as Breast Boils or Breast Cancer
Due to the similarity in appearance, ingrown hairs under the breast can sometimes be mistaken for breast boils or even inflammatory breast cancer, both of which can present as a lump or swelling in the breast area. Misdiagnosis can lead to unnecessary stress and inappropriate treatment. Therefore, correct diagnosis is of utmost importance.
D. Correct Diagnosis
Correct diagnosis of an ingrown hair under the breast typically involves a visual inspection by a healthcare professional. In some cases, a dermatologist may take a skin scraping or perform a biopsy to rule out other skin conditions. Recognizing the common symptoms and consulting with a professional is crucial for correct diagnosis and treatment.
Treatment Options for Ingrown Hair under the Breast
A. Warm Compress
Applying a warm compress to the affected area can help soothe an ingrown hair under the breast [9]. The warmth from the compress aids in reducing inflammation and can soften the skin, potentially helping the ingrown hair to surface [10].
B. Topical Treatments
Over-the-counter topical treatments, such as creams, gels, and lotions containing salicylic acid or benzoyl peroxide, can aid in treating ingrown hairs [11]. These substances work by exfoliating the skin, reducing inflammation, and helping to free the trapped hair.
C. Antibiotics for Infected Ingrown Hairs
In cases where an ingrown hair under the breast becomes infected, potentially signaled by persistent redness, swelling, and the presence of pus, a healthcare provider may prescribe a course of topical or oral antibiotics. This is intended to eliminate the infection caused by bacteria, commonly Staphylococcus aureus [12].
D. Professional Medical Care
If home remedies and over-the-counter treatments are ineffective, it might be necessary to seek professional medical care. A dermatologist can safely extract the ingrown hair or, in severe cases, might suggest treatments like laser hair removal or steroid injections to reduce inflammation.
Prevention of Ingrown Hair under the Breast
A. Proper Hair Removal
Adopting proper hair removal techniques can significantly help prevent ingrown hairs under the breast. It is advisable to shave in the direction of hair growth, use a sharp single-blade razor, and avoid pulling the skin taut while shaving. If waxing is the preferred method, it is crucial to exfoliate the skin beforehand to prevent the hair from growing back into the skin.
B. Lifestyle Changes
Simple lifestyle changes such as wearing breathable, loose-fitting clothing, especially around the breast area, can reduce friction and prevent the development of ingrown hairs [13]. Moreover, maintaining good hygiene by regularly cleansing and gently exfoliating the area under the breast can help keep the hair follicles clear.
C. Regular Check-ups
Regular skin check-ups can also help in the early detection and prevention of ingrown hairs. By consulting with a dermatologist or healthcare provider, individuals can get personalized advice and treatment options based on their skin type and hair growth patterns.
Conclusion
A. Recap of Essential Care
Understanding the symptoms, causes, and appropriate treatment options for ingrown hair under the breast is the cornerstone of managing this condition. From applying a warm compress and using topical treatments to seeking professional medical care when necessary, these measures provide a comprehensive approach to treating ingrown hair under the breast.
B. Re-emphasizing the Importance of Awareness and Early Treatment
The potential misdiagnosis of an ingrown hair under the breast as a breast boil or even breast cancer underlines the importance of awareness and early treatment. Regular check-ups, awareness of one’s own body, and swift action when symptoms occur can prevent complications and ensure appropriate and effective treatment.